Aardonyx Guide:
Aardonyx was an early dinosaur that lived in South Africa about 200 million years ago.
Aardonyx was an early dinosaur that lived in South Africa about 200 million years ago.

Apatosaurus is a massive dinosaur from the Late Jurassic period, famous for its long neck and gentle demeanor. You’d be amazed to learn it could grow up to 75 feet and weigh around 22 tons! This herbivorous giant thrived in North America, using its peg-like teeth to strip leaves from high vegetation. Discovered in 1877 during the Bone Wars, the name means “deceptive lizard.” Apatosaurus played a key role in prehistoric ecosystems and showcased unique features like a heart-shaped ribcage. If you’re curious about its history, habitat, and more fascinating facts, you’ll want to explore further.
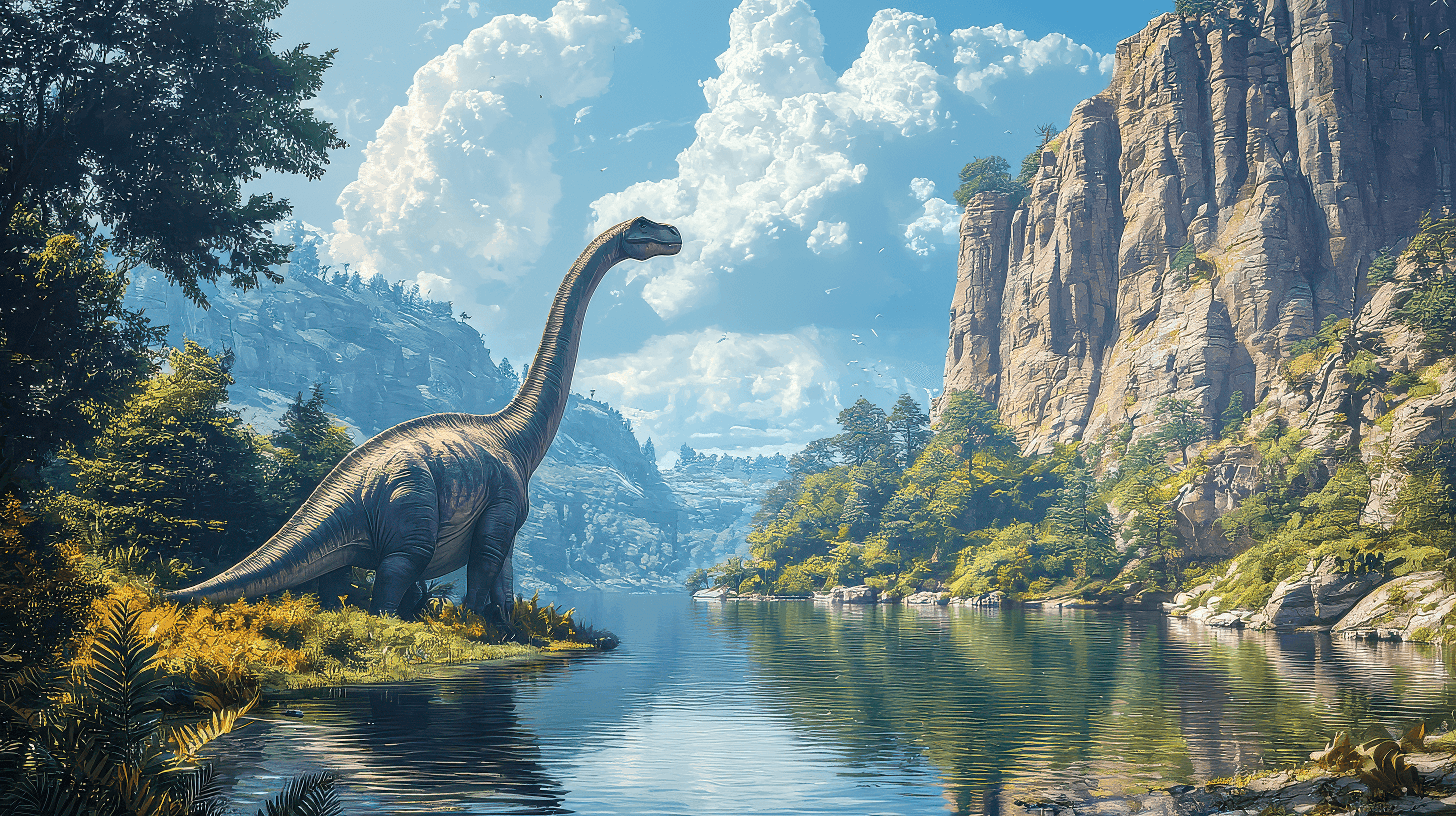
The Apatosaurus, a massive dinosaur from the Late Jurassic period, captures your imagination with its impressive size and gentle nature.
This sauropod, recognized for its long neck and massive body, was primarily herbivorous, feeding on the abundant vegetation of its time characterized by long necks.
Comprehending this species is crucial, as it plays an important role in its ecosystem and reflects the complexity of prehistoric life.
Let’s explore its significance and what makes the Apatosaurus a fascinating subject of study.
Hailing from the Late Jurassic Period, Apatosaurus, often dubbed the “deceptive lizard,” stands out as one of the most iconic sauropod dinosaurs. This massive creature could reach lengths of up to 75 feet and weighed around 22 tons. It thrived in diverse habitats across North America, primarily foraging on high vegetation thanks to its elongated neck.
Apatosaurus behavior is characterized by its gentle nature, and it often socialized in herds, which provided safety in numbers against predators. These dinosaurs likely engaged in nurturing behaviors, as evidence suggests they exhibited parental care during reproduction.
Their diet mainly consisted of leaves and other plant matter, which they could efficiently strip from tall trees.
Despite their impressive size, Apatosaurus possessed a relatively small brain, weighing only about 4 ounces. This contrast highlights their herbivorous lifestyle, as they relied more on instinct and social structures than complex problem-solving.
Comprehending Apatosaurus socialization and habitat is essential for appreciating how these magnificent creatures once roamed the Earth, contributing to their ecosystems as gentle giants of the Jurassic terrain.
| Aspect | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Fossil Significance | Key to grasping sauropod evolution | Reveals ancient biodiversity |
| Ecological Impact | Influenced vegetation and ecosystems | Demonstrates herbivore roles |
| Educational Value | Central to paleontological studies | Engages students in science |
| Cultural Representation | Featured in media and literature | Inspires interest in dinosaurs |
| Evolutionary Insights | Offers clues to the adaptation and survival | Improves knowledge of species |
Apatosaurus continues to serve as a focal point for education and research, making it a essential piece of our comprehension of prehistoric life. Its legacy helps us appreciate how ancient creatures shaped their world, ensuring they remain a fascinating subject for generations to come.
In 1877, you’ll find that Apatosaurus was first described by O.C. Marsh after fossils were discovered in Colorado.
The name itself means “deceptive lizard,” reflecting its misleading resemblance to other reptiles.
Comprehending the key paleontologists involved in its discovery helps you appreciate the expedition of this iconic dinosaur.
Discovering the Apatosaurus in 1877 marked a significant moment in paleontology, as O.C. Marsh unearthed the first fossils during the Bone Wars. This competitive period ignited a race among paleontologists to uncover and classify dinosaur remains. The initial excavation took place at Como Bluff, Wyoming, a site renowned for its rich Jurassic deposits.
Marsh utilized innovative excavation techniques that improved fossil preservation, allowing for a clearer comprehension of these prehistoric giants.
The discovery timeline was vital, as the Apatosaurus was recognized and named before Brontosaurus was proposed in 1879, solidifying its place in scientific literature. This historical context underlines the paleontological significance of the Apatosaurus, which, in spite of initial confusion regarding its classification, helped shape our comprehension of sauropods.
Elmer Riggs’ misclassification of Apatosaurus as a juvenile Brontosaurus in 1903 only added to the intrigue surrounding this species.
In the end, the Apatosaurus stands as a symbol of the evolving nature of paleontology and the importance of rigorous scientific methods in uncovering the mysteries of the past. Grasping its discovery helps you appreciate the progression of paleontological research and the significance of these findings.
The name “Apatosaurus,” which translates to “deceptive lizard,” reflects the confusion that surrounded its classification in the late 19th century. Its name etymology comes from Greek roots, where “apatos” means “deceptive” and “sauros” means “lizard.” This linguistic significance highlights the initial misidentifications that took place during the era.
In 1877, paleontologist O.C. Marsh first described the genus, marking a pivotal moment in the historical context of dinosaur studies. Nevertheless, Apatosaurus was often confused with another dinosaur, Brontosaurus, leading to a long-standing debate about naming conventions within paleontology. The name “Apatosaurus” was published first, and in spite of the popularity of “Brontosaurus,” it retained its official designation.
In 2015, further research confirmed that Apatosaurus and Brontosaurus are distinct genera, clarifying its place in the dinosaur family tree. This resolution not only underscores the importance of accurate classification but additionally enriches our comprehension of these magnificent creatures.
Ultimately, the evolution of Apatosaurus’s name illustrates the intricacies of scientific discovery and the ongoing quest for clarity in our grasp of prehistoric life.
O.C. Marsh, a prominent paleontologist, first described Apatosaurus in 1877 after his groundbreaking discoveries in the late 19th century. This colossal dinosaur’s name, meaning “deceptive lizard,” gained official recognition, overshadowing the later term “Brontosaurus.”
Nevertheless, early skull misidentification led to confusion between these two genera, which persisted for decades. Marsh’s contributions laid the groundwork for insight into Apatosaurus, but it wasn’t until 1978 that a long-lost skull was rediscovered at the Carnegie Museum. This significant find clarified the dinosaur’s physical characteristics and corrected many misconceptions.
The rediscovery played a vital role in resolving long-standing classification debates surrounding Apatosaurus. In 2015, a thorough study analyzing 81 sauropod skeletons confirmed that Apatosaurus is certainly a distinct genus, separate from Brontosaurus.
This research highlighted the importance of ongoing paleontologist contributions in refining our comprehension of these magnificent creatures. As you explore deeper into the realm of Apatosaurus, keep in mind the evolving nature of paleontology, where new discoveries can reshape our knowledge and appreciation of these ancient giants.
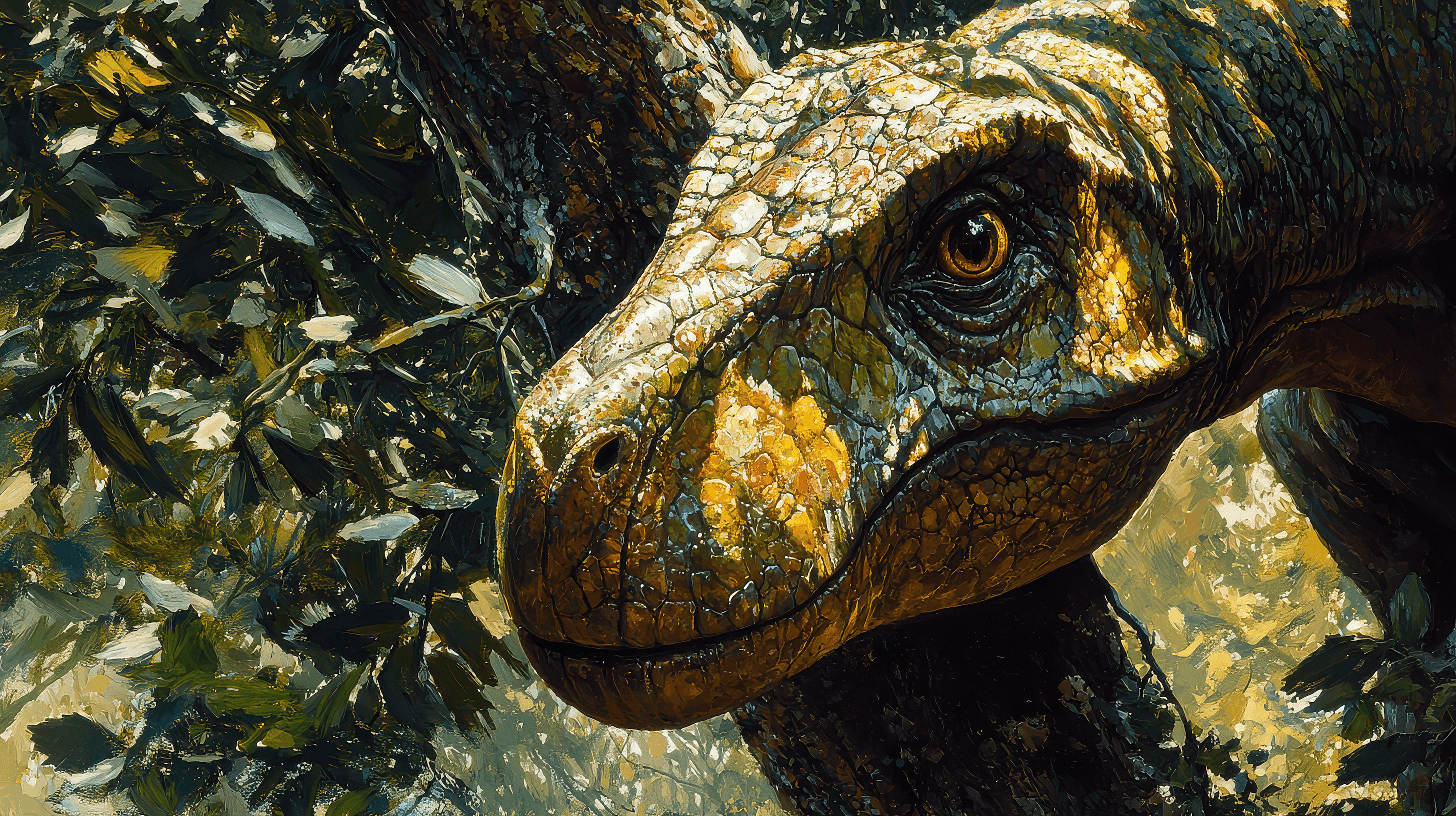
When you think about the Apatosaurus, its massive size and weight immediately stand out, as it could reach lengths of up to 75 feet and weigh around 41 tons.
This sauropod is characterized by its long neck, which could extend to great lengths, enabling it to
access high foliage and diverse feeding areas, a common trait among sauropod adaptations.
You’ll likewise notice its distinctive features, like the peg-like teeth, which helped it thrive in its environment.
Coloration theories add another layer of intrigue, sparking your imagination about what this gentle giant might’ve looked like in its natural habitat.
Measuring up to an astonishing 23 meters (about 75 feet) in length, Apatosaurus stands as one of the largest land animals to ever roam the Earth. Its massive size invites awe and curiosity, prompting researchers to explore its growth patterns and weight estimations through various measurement techniques.
To better comprehend this gentle giant, consider these key points:
Through ongoing research, scientists continue to refine our comprehension of Apatosaurus, shedding light on its incredible size and weight that defined its existence in the Jurassic period.
Apatosaurus isn’t merely impressive in size; its distinctive physical characteristics set it apart from other dinosaurs. One of its unique adaptations is its long neck, which allows it to reach high vegetation, showcasing effective feeding strategies. The slender head, equipped with peg-like teeth, is perfect for stripping leaves, whereas the massive, pillar-like legs support its enormous weight, reflecting an efficient skeletal structure.
Here’s a visual representation of some distinctive features:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Length & Weight | Up to 23 meters (75 feet) and 41 tonnes |
| Leg Structure | Pillar-like, similar to modern elephants |
| Tail | Long and whiplike, possibly producing sound |
| Ribcage | Heart-shaped cross-section |
Environmental influences shaped its physical traits, enabling it to thrive in various habitats. Furthermore, Apatosaurus likely engaged in social interactions during foraging in herds, promoting safety and efficient feeding. These characteristics not only define the Apatosaurus but likewise highlight its role within the Jurassic ecosystem.
Coloration theories surrounding the Apatosaurus remain speculative, yet intriguing to explore. While we lack definitive evidence, several ideas offer insight into how this massive dinosaur might’ve appeared.
It’s believed that the Apatosaurus could have developed coloration patterns that aided in survival and social interaction.
Fossilized skin impressions hint at scaly textures, which could indicate specific coloration patterns akin to modern reptiles.
By studying related dinosaur species with preserved coloration, researchers can gain indirect insights into the potential hues of the Apatosaurus.
Though direct evidence remains elusive, these theories provide an engaging glimpse into how this gentle giant may have navigated its surroundings, blending in with its environment while connecting with its herd.
When you look at the classification of Apatosaurus, you’ll find it belongs to the genus Apatosaurus, with A. louisae being the most prominent species.
Comprehending its taxonomic relationships helps highlight its evolutionary connections to other sauropods. As research progresses, new findings continue to reshape how we view its place in the prehistoric world.
When you explore the taxonomic classification of Apatosaurus, you’ll find it fits into a well-defined hierarchy.
It’s categorized under the Kingdom Animalia, Phylum Chordata, and Class Reptilia, among other classifications.
Comprehending these categories helps clarify its place in the dinosaur family tree and its relationships to other sauropods.
What defines the Apatosaurus in the grand scheme of life on Earth? This remarkable dinosaur belongs to the kingdom Animalia, showcasing its multicellular structure and heterotrophic nature.
Understanding its evolution helps highlight its significance.
The Apatosaurus, a fascinating member of the dinosaur family, belongs to the phylum Chordata, which encompasses all animals that display a notochord at some stage in their development.
This classification highlights key phylum characteristics, showcasing chordate evolution and vertebrate diversity.
As part of important clades, Apatosaurus fulfills crucial ecological roles, exemplifying the importance of preserving such remarkable creatures in our planet’s history.
As part of the phylum Chordata, Apatosaurus is classified under the class Sauropodomorpha. This classification reflects its unique features and evolutionary significance, including:
Understanding these aspects helps you appreciate the significance of this remarkable dinosaur in the broader context of paleontology.
Apatosaurus falls under the order Sauropoda, a classification that encompasses some of the largest land animals ever to roam the Earth. This gentle giant adapted to diverse habitats, displaying unique behaviors like socialization in herds. Its reproductive habits guaranteed species continuity, as its long neck aided in foraging. Let’s explore its classification further:
| Feature | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Behavior | Gentle herbivore | Maintains ecosystem balance |
| Habitats | Diverse environments | Supports survival strategies |
| Adaptations | Long neck, strong tail | Efficient foraging and defense |
| Reproduction | Lay eggs in nests | Secures species propagation |
| Socialization | Herd living | Improves protection from predators |
Within the fascinating world of dinosaurs, Apatosaurus is classified under the suborder Sauropodomorpha.
This suborder features:
Understanding these suborder characteristics helps you appreciate Apatosaurus’s role in prehistoric ecosystems and its relationship with related suborders.
Often recognized for its massive size and gentle demeanor, Apatosaurus belongs to the family Sauropodidae.
This family exhibits fascinating family dynamics, showcasing evolutionary adaptations that improve survival. Their social interactions are evident in herd behavior, allowing these giants to forage together.
Furthermore, their reproductive strategies guarantee the continuity of their lineage, emphasizing the importance of cooperation within their social structure.
Typically classified under the genus Apatosaurus, this fascinating group of sauropods showcases some of the most remarkable features of the dinosaur world.
These aspects make Apatosaurus an intriguing subject of study.
Apatosaurus, a remarkable member of the sauropod family, showcases a fascinating classification within the dinosaur kingdom. This species, particularly Apatosaurus louisae, reflects unique adaptations for foraging and locomotion in its ecological niche. Misclassifications have been clarified, revealing its distinct behavior and relationships within the clade Sauropodamorpha.
| Species Name | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Apatosaurus louisae | Long neck, herbivorous diet |
| Sauropodamorpha | Close ties to other sauropods |
| Endangered Status | Crucial role in ecosystem health |
Within the vast family of sauropods, you’ll find Apatosaurus sharing close ties with several other remarkable dinosaurs.
These Apatosaurus relatives, all Jurassic herbivores, belong to a diverse group characterized by their enormous sizes and unique adaptations.
When you examine sauropod comparisons, you’ll notice distinct features that set each species apart while highlighting their evolutionary connections.
Understanding these related species enriches your knowledge of dinosaur phylogeny and the complex relationships among these magnificent creatures.
Each one plays a crucial role in the larger narrative of Jurassic ecosystems, showcasing the diversity and adaptability of sauropods.
The classification of Apatosaurus reveals fascinating insights into its evolutionary relationships within the sauropod family. This colossal dinosaur, first described by O.C. Marsh in 1877, showcases a complex ancestral lineage that links it to other large herbivores like Brachiosaurus and Diplodocus.
Recent phylogenetic analysis has confirmed that Apatosaurus and Brontosaurus are distinct genera, clearing up past confusion.
As you explore deeper into its evolutionary adaptations, you’ll see how Apatosaurus thrived during the late Jurassic period, approximately 156 to 151 million years ago. Fossil evidence indicates that it coexisted with various other dinosaurs, highlighting crucial speciation events that shaped its development.
During genetic studies show limited genetic diversity among its variants, comprehending these relationships helps clarify how environmental factors influenced its adaptations and survival strategies.
In essence, studying Apatosaurus isn’t just about one dinosaur; it’s a window into the broader narrative of sauropod evolution. By examining its classification, you gain a clearer picture of how these magnificent creatures interacted with their ecosystems and adapted over millions of years.
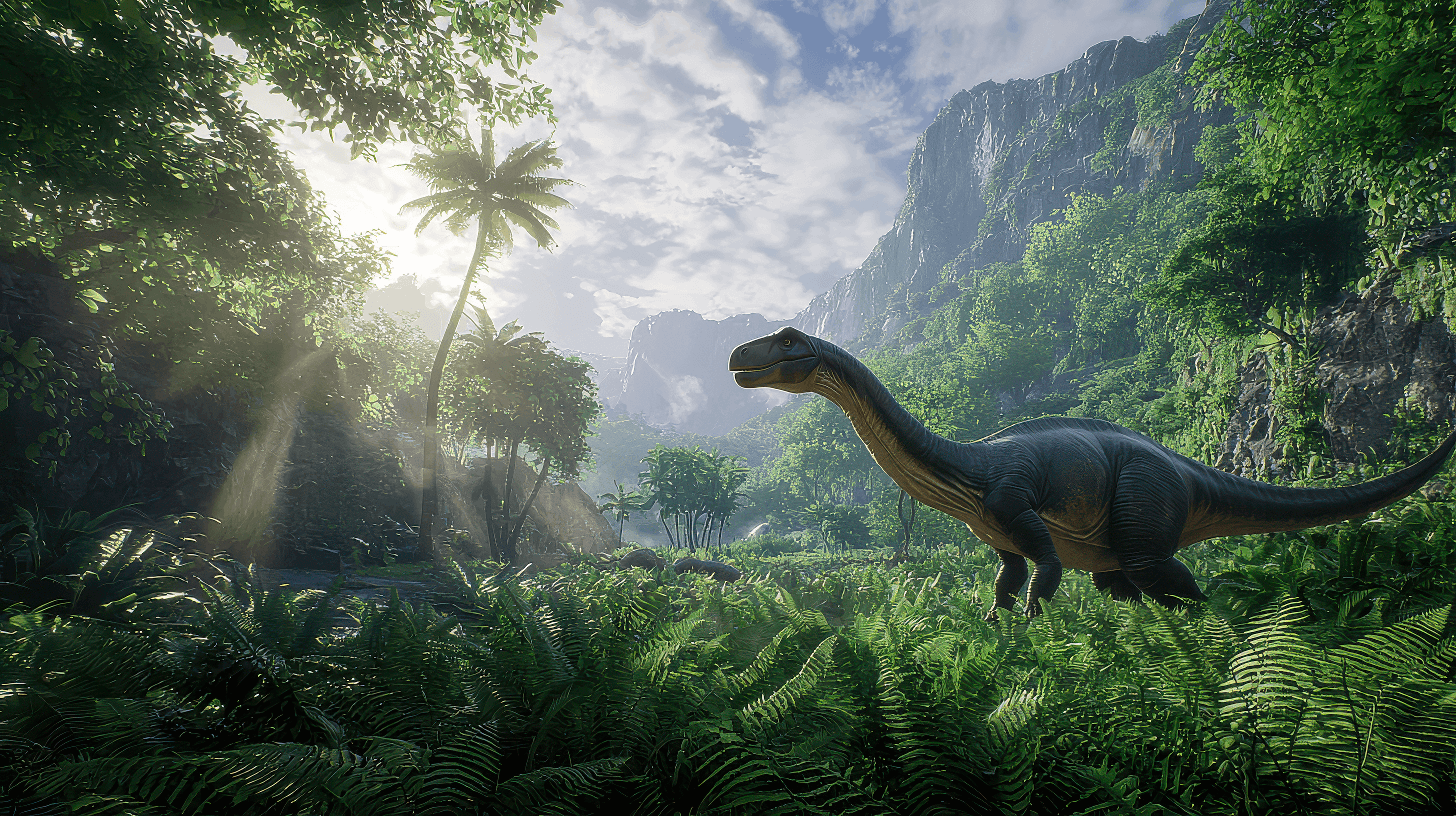
The Apatosaurus thrived during the Late Jurassic period, roughly 156 to 151 million years ago, in what’s now North America.
You’ll find fossil evidence primarily in the western United States, especially at sites like Como Bluff in Wyoming.
This massive herbivore roamed diverse habitats, such as lush floodplains, which provided the vegetation it needed to support its giant frame.
When did the Apatosaurus roam the Earth? This colossal sauropod thrived during the Late Jurassic Period, about 156 to 151 million years ago.
Fossil evidence reveals that Apatosaurus primarily inhabited lush, forested environments across North America, particularly in regions like Colorado and Wyoming.
During this time, you’d find Apatosaurus engaging in various crucial activities:
With its long neck and sturdy build, Apatosaurus effectively foraged for plants as it avoided danger from larger predators.
Their reproductive strategies involved nurturing young in a communal setting, promoting a sense of security.
Fossils of the Apatosaurus have primarily emerged from North America, particularly in the Morrison Formation, a rich geological site that’s become a treasure trove for paleontologists. This area spans several states, including Colorado, Wyoming, and Utah, showcasing notable fossil distribution patterns.
During the Late Jurassic Period, approximately 156 to 151 million years ago, Apatosaurus thrived in a warm, humid environment filled with lush vegetation. The fossil evidence suggests that these gentle giants inhabited floodplain ecosystems, which provided abundant plant life for their diet.
Important regional fossil hotspots like Como Bluff in Wyoming have yielded numerous specimens, greatly enhancing our comprehension of sauropod diversity. Analyzing geographic diversity implications, researchers can better grasp how Apatosaurus interacted with other species within its ecosystem.
This environmental influences analysis contributes to paleoecological reconstructions, revealing how these magnificent dinosaurs adapted to their habitats. By studying the distribution of Apatosaurus fossils, you gain insight into the interconnectedness of species and the ecological dynamics of the Late Jurassic period, highlighting the importance of these findings for comprehending dinosaur life and their environments.
Grasping the paleoenvironment of the Apatosaurus reveals a lively world teeming with life during the Late Jurassic Period. This colossal herbivore thrived in a time marked by significant paleoenvironmental changes, influenced by diverse climate conditions.
Its habitat, primarily located in what’s now North America and parts of Europe, featured a variety of vegetation types, which provided abundant food sources. You’d find Apatosaurus wandering through lush forests and open plains, showcasing the habitat diversity that supported such large creatures.
Key aspects of its environment included:
The Apatosaurus adapted remarkably well to its surroundings, with a sturdy skeletal structure that supported its immense weight.
As you explore this ancient world, appreciate how the Apatosaurus not only coexisted with other species but additionally influenced the ecosystem through its feeding habits and social behaviors. Comprehending these dynamics helps you grasp the complexity of life in the Late Jurassic and the role of the Apatosaurus within it.
The paleobiology of the Apatosaurus reveals fascinating insights into the life and behavior of this enormous sauropod. Known for its impressive size, Apatosaurus developed several herbivorous adaptations that allowed it to thrive in its environment. With a long neck, it could reach high vegetation, which was essential for its feeding strategies.
Fossil evidence indicates that Apatosaurus likely foraged in herds, showcasing social behavior that improved its chances of survival against predators. This herd mentality likely encouraged communication and cooperation among individuals, much like modern-day herbivores.
Despite its massive size, the Apatosaurus had a relatively small brain, weighing only about 4 ounces. This reflects its brain evolution, suggesting that its simple lifestyle didn’t necessitate complex cognitive functions.
Here’s a quick overview of key aspects of Apatosaurus:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Size | Up to 75 feet long, weighing 41 tons |
| Locomotion Mechanics | Four pillar-like legs support its weight |
| Feeding Strategy | Reached high vegetation in herds |
Understanding these characteristics helps us appreciate the Apatosaurus’s role in its ecosystem and its unique adaptations to survive in the Late Jurassic period.
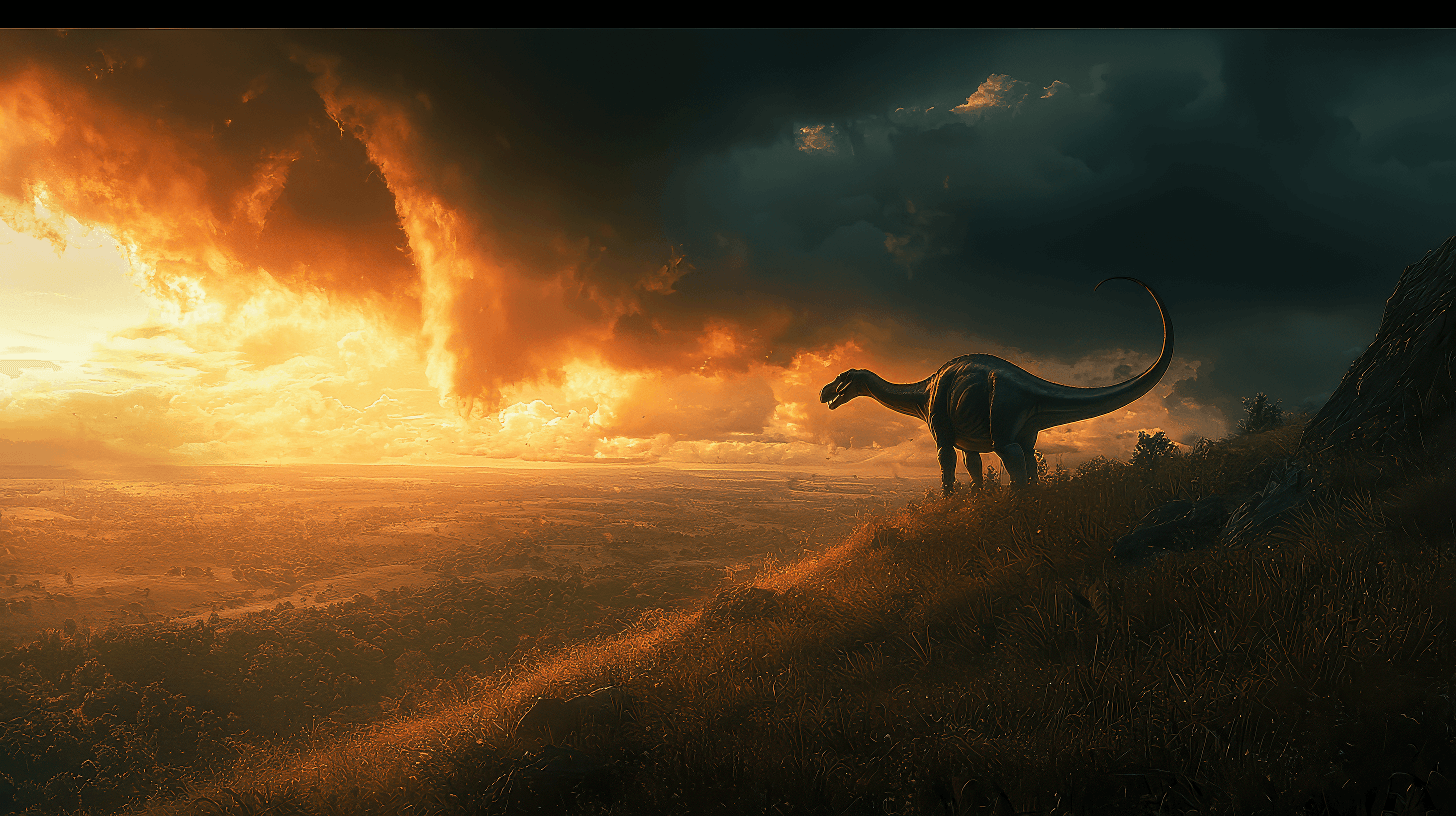
When you think about the locomotion of the Apatosaurus, picture its massive, pillar-like legs supporting a weight of up to 41 tonnes.
Its long neck and flexible tail not only aided it in reaching high vegetation but additionally contributed to its balance and movement patterns.
Let’s explore how these features influenced its gait, speed, and adaptations to its environment.
Apatosaurus showcases a remarkable gait that reflects its massive size and weight, which can reach up to 41 tonnes. This colossal dinosaur exhibited unique gait mechanics, characterized by its pillar-like legs that supported its considerable bulk.
You’d observe that its locomotion efficiency was optimized for slow, deliberate movements, allowing it to traverse vast distances in search of vegetation.
Key features of its movement include:
These adaptations not merely improved its movement speed but additionally had significant evolutionary implications, allowing Apatosaurus to thrive in various environments.
With its massive frame and unique adaptations, speed estimates for Apatosaurus reveal that this colossal dinosaur could reach around 10 miles per hour (16 kilometers per hour) when moving briskly.
In spite of its size, Apatosaurus showcased impressive speed adaptations that allowed for efficient locomotion across varied terrain. Its long legs and strong skeletal structure contributed to this locomotive efficiency, enabling it to navigate different environments as it foraged for vegetation.
Although the weight of approximately 26 tons likely limited its maximum speed compared to smaller dinosaurs, Apatosaurus had evolved specific movement strategies suited to its herbivorous lifestyle.
Instead of sprinting away from predators, it utilized a unique gait, moving both legs on one side of its body followed by the legs on the other, similar to modern-day elephants.
This method allowed for steady browsing rather than rapid escape, reflecting the evolutionary advantages of being a large, peaceful creature in its ecosystem.
Inhabiting the lush scenery of the Jurassic period, Apatosaurus displayed remarkable terrestrial adaptations that allowed it to thrive as a massive herbivore. With its robust skeletal structure and massive, pillar-like legs, it efficiently supported its immense weight during traversing land environments.
Consider the following features that underline its adaptations:
These adaptations underscore Apatosaurus’s role in its ecosystem. Although some might draw aquatic comparisons, it’s clear that this gentle giant was perfectly suited for life on land.
Its adaptations not only allowed it to reach diverse food sources but likewise to maintain stability and protection during movement in herds. By comprehending these traits, you gain insight into how Apatosaurus thrived in its environment and how it became an iconic figure of the Jurassic period.
When you think about the sensory capabilities of the Apatosaurus, it’s fascinating to contemplate how its brain size and structure influenced its perception of the world.
With its broad field of vision and potential for sharp olfactory abilities, this giant could have effectively navigated its environment.
Let’s explore how these traits helped it survive in the Jurassic terrain.
The Apatosaurus, in light of its massive size, had a surprisingly small brain that weighed only about 4 ounces (125 grams). This small brain size reflects its herbivorous diet and lifestyle, leading to certain cognitive limitations. Brain evolution in large herbivores like the Apatosaurus often favors instinctual behavior over complex cognitive functions.
While you might think a larger brain would mean a more intelligent animal, in the Apatosaurus’s case, it relied on its sensory capabilities to survive. The heightened sense of smell and hearing played fundamental roles in staying alert to threats.
In spite of the cognitive limitations posed by its small brain, the Apatosaurus thrived in its ecosystem, using instinct and sensory adaptation to navigate the challenges of its prehistoric world. Comprehending these aspects of the Apatosaurus’s brain can give you a clearer picture of how it lived and interacted with its environment.
Comprehension of the sensory capabilities of the Apatosaurus sheds light on how this colossal herbivore navigated its environment. With a small brain weighing about 4 ounces, its visual processing likely relied on basic cues rather than complex imagery. This means it probably used its size and position in herds to forage effectively for vegetation, focusing on movement and color contrasts.
While there’s no direct evidence of its hearing, Apatosaurus’s large body suggests it had a well-developed auditory perception system, allowing it to detect low-frequency sounds in its surroundings. This ability would have been essential for staying alert to potential dangers.
As for olfactory detection, though not thoroughly documented, it’s reasonable to think Apatosaurus had a sharp sense of smell. This would help it locate food sources and sense nearby predators, which is critical for ecological survival in a world filled with threats.

Thermoregulation in Apatosaurus showcases the fascinating adaptations this massive herbivore developed to thrive in its environment. To maintain a stable body temperature, Apatosaurus likely relied on a combination of basking behavior and strategic environmental adaptations. Its immense size, reaching up to 41 tonnes, provided a lower surface area-to-volume ratio, which helped with heat retention in cooler climates.
Consider these key thermoregulation strategies:
These adaptations allowed Apatosaurus to effectively manage its body temperature as it foraged in various environments.
In relation to diet, the Apatosaurus is a strict herbivore, primarily feasting on high vegetation.
With its long neck, it reaches for leaves from tall trees, showcasing specialized feeding adaptations.
Its leaf-shaped teeth, designed for slicing through foliage, further illustrate how this dinosaur was well-equipped for its herbivorous lifestyle.
Comprehending its dietary preferences and strategies can reveal how this massive dinosaur thrived in its environment, particularly in habitats with abundant vegetation where it could exploit both high and low plant sources, as seen in paleoecological adaptations.
Apatosaurus thrived on a diet of leaves and vegetation, thanks to its long neck that let it reach high into the treetops. As a herbivore, its feeding behavior was particularly adapted to strip leaves with its peg-like teeth, which were perfect for processing plant material. This dietary adaptation allowed Apatosaurus to effectively meet its substantial energy needs, as its massive size required a large quantity of plant matter.
When you consider its foraging strategies, it’s clear that Apatosaurus likely foraged in herds. This not only improved their ability to locate food but likewise provided protection against predators.
Here are some key aspects of Apatosaurus’s dietary habits:
These features highlight the herbivore evolution of Apatosaurus and its significant role in the ecosystem, maintaining balance through its unique feeding strategies and adaptations.
The massive Apatosaurus thrived on a varied diet primarily composed of leaves and soft plant materials. With its long neck, this gentle giant could reach high tree canopies and shrubs, allowing it to access food that many other dinosaurs couldn’t. Your comprehension of its foraging techniques reveals that Apatosaurus spent time both browsing tall foliage and searching on the ground for low-growing plants.
Dietary variations were fundamental to meet its substantial nutritional needs, estimated at around 1,000 pounds of vegetation daily. It had specific plant preferences, favoring tender leaves and soft materials over tougher plants. Seasonal feeding likewise played a role in its diet; during different times of the year, the availability of certain vegetation would influence its choices.
Fossil evidence indicates that Apatosaurus’s peg-like teeth were designed for stripping leaves rather than chewing, reflecting its need to consume large quantities of food quickly. By adapting its foraging behaviors and dietary habits, Apatosaurus could thrive in diverse environments, showcasing its role as a vital herbivore in the Jurassic ecosystem.
With its impressive adaptations for feeding, Apatosaurus showcases a remarkable ability to thrive in its environment. This colossal herbivore developed several unique strategies to meet its substantial dietary needs. Utilizing its long neck, it could reach high vegetation, allowing for effective plant selection.
These herbivorous adaptations allowed Apatosaurus to exploit its environment efficiently. By focusing on high foliage, it minimized competition with other plant-eaters.
The combination of its physical traits and social foraging behaviors guaranteed that this giant could thrive in the lush terrains of the Late Jurassic period. Comprehending these feeding adaptations gives you insight into how Apatosaurus successfully navigated its world, highlighting its role in prehistoric ecosystems.
When you think about Apatosaurus, consider their social behavior and how it shaped their survival.
These massive creatures likely foraged in herds, using group dynamics to stay safe from predators.
You’ll see that their interactions and strategies were key to thriving in their environment.
Among the fascinating behaviors of Apatosaurus, evidence of social interaction stands out, revealing how these gentle giants thrived in their environment. Their herd dynamics played an essential role in enhancing survival, as foraging in groups provided safety against predators. The social structures likely included family groups, promoting cooperative feeding and protection.
Here are some key aspects of their social behavior:
Such behaviors indicate that Apatosaurus wasn’t just a solitary browser but a social creature thriving in a complex environment.
Apatosaurus relied heavily on effective foraging strategies to meet its substantial dietary needs. This massive herbivore primarily sought low-lying vegetation, using its long neck to access a variety of plants. Its foraging behavior was essential, as it needed to consume large amounts of foliage to sustain itself.
By foraging in herds, Apatosaurus benefited from herd dynamics, allowing individuals to stay safer from predators. The social structure of these dinosaurs played a significant role in their survival. When foraging together, they could effectively communicate and detect potential threats, enhancing their chances against predator interactions.
Their dietary strategies included using peg-like teeth to strip leaves, which were abundant in the Late Jurassic environment. Apatosaurus additionally had specific feeding adaptations that supported its lifestyle.
During foraging in groups, these gentle giants could utilize their strong tails defensively, warding off potential threats. This combination of herd behavior and feeding adaptations fulfilled their dietary needs and guaranteed their safety in a world filled with dangers.
Foraging in herds not solely helped Apatosaurus locate food more efficiently but furthermore encouraged a complex social structure that likely played a vital role in their survival. This herd behavior nurtured social interactions, allowing these gentle giants to thrive in their environment.
Consider the following aspects of their group dynamics:
Although solitary behavior might’ve occurred, especially among younger individuals, the advantages of herding likely outweighed the benefits of being alone.
When you think about Apatosaurus reproduction, consider how these giants likely used internal fertilization and laid large clutches of eggs in nests.
You’ll find that young Apatosaurus grew swiftly, reaching impressive sizes quickly to avoid predators.
Comprehending their growth rates and life stages helps paint a clearer picture of how these magnificent creatures thrived in their environment.
In the domain of dinosaurs, comprehending the reproductive habits of the Apatosaurus reveals fascinating insights into their life cycle.
These gentle giants likely engaged in elaborate mating displays to attract partners, much like modern-day animals. They laid eggs in nests, with findings suggesting clutches could contain several dozen eggs, indicating a strategy for reproductive success.
Key aspects of their reproductive habits include:
While much remains speculative, these insights help paint a picture of the reproductive strategies that supported the survival of the Apatosaurus throughout its lifecycle.
Situated within the intriguing world of dinosaur reproduction, egg and nest information sheds light on the early life of the Apatosaurus. Like many sauropods, Apatosaurus likely reproduced by laying eggs, even though no specific nests have been identified.
Fossil evidence suggests that these giants may have exhibited colony nesting behavior, which would have provided safety in numbers during the vulnerable egg-laying period.
The eggs, measuring around 12 inches (30 cm) in diameter, were likely soft-shelled, similar to those of modern reptiles. This egg size indicates that the hatching process could have been delicate, requiring favorable conditions to guarantee the survival of the young.
Once hatched, juvenile Apatosaurus entered a critical phase of rapid development, needing to consume large quantities of foliage to support their growth.
In the first years of life, these young dinosaurs may have grown several pounds per day, an indication of their impressive juvenile development. This rapid growth would have been crucial for them to attain their massive adult size and to thrive in their prehistoric habitats.
Comprehending these aspects of their reproduction helps us appreciate the life cycle of the Apatosaurus.
Comprehension of the growth rates and life stages of the Apatosaurus reveals how this magnificent creature developed throughout its life. These gentle giants experienced rapid growth spurts during their early years, quickly gaining height and weight. By consuming a juvenile diet rich in leafy vegetation, they supported their impressive growth and massive size.
As they matured, Apatosaurus reached reproductive maturity around 10-15 years of age, which is typical for large sauropods. This early maturity allowed for a long reproductive span, contributing to their longevity factors. Fossil evidence shows that adults could live up to 70-80 years, giving them ample time to reproduce and thrive.
Their growth followed seasonal patterns, much like modern reptiles. This means that Apatosaurus likely experienced periods of accelerated growth during favorable seasons.
Understanding these aspects of their growth and development helps us appreciate the life cycle of the Apatosaurus.
As you explore the realm of Apatosaurus, it’s essential to understand the threats it faced from predators like Allosaurus and Ceratosaurus.
These massive herbivores developed unique defense strategies, including potent tail strikes and social herding behavior, to protect themselves.
Let’s take a closer look at how these adaptations helped them survive in a challenging environment.
The Apatosaurus, in light of its massive size, faced threats from formidable predators during the late Jurassic period. While its impressive length of up to 76 feet and weight of around 26 tons offered some protection, it wasn’t invulnerable. Large carnivores like Allosaurus and Torvosaurus posed real risks, creating complex predator-prey interactions that influenced the Apatosaurus’s survival strategies.
These evolutionary pressures led the Apatosaurus to develop defensive adaptations, such as foraging in groups. Living in herds made it more difficult for predators to isolate an individual, which was vital in their habitat competition.
In spite of its size, the Apatosaurus had to remain vigilant, realizing that its peaceful nature didn’t eliminate the threat of hungry carnivores. The balance between being a gentle giant and a potential prey species shaped its existence in a world filled with dangers.
Facing numerous threats from predators like Allosaurus and Torvosaurus, the Apatosaurus developed a range of effective defense strategies and adaptations to boost its survival. Its impressive size—up to 41 tonnes—served as a significant predator deterrence, making it a challenge for most carnivores to take on.
Apatosaurus’s long, robust tail acted as a vital tail defense mechanism, capable of delivering powerful strikes to potential attackers. Furthermore, the animal’s pillar-like legs allowed it to move quickly, escaping danger when needed.
Social herd dynamics played an important role in its defense strategy. By foraging in groups, Apatosaurus individuals could better protect one another, as predators found it harder to target a single animal. Their browsing strategies likewise helped them access high vegetation, reducing competition and avoiding ground-level threats.
Here’s a table summarizing these adaptations:
| Adaptation | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Size Advantages | Huge body size | Predator deterrence |
| Tail Defense Mechanisms | Long and powerful tail | Offensive and defensive weapon |
| Social Herd Dynamics | Group foraging | Improved safety |
| Quick Movement | Strong legs for swift escape | Evasion of predators |
| Browsing Strategies | Access to high vegetation | Reduced competition |
Throughout their lives, Apatosaurus encountered various health challenges, as revealed by paleopathological studies of their fossils. These fascinating findings shed light on the disease impact and the overall bone health of this giant dinosaur.
You’ll find that skeletal analysis has uncovered various issues, including:
These studies highlight how environmental stress could have played a significant role in the Apatosaurus’s life. Their herbivorous diet, although vital for sustenance, may have led to dental issues, affecting their feeding behavior over time.
The evidence of trauma and disease suggests that these creatures faced a range of challenges, impacting their growth patterns and longevity. By comprehending these health challenges, we gain a deeper appreciation for the resilience of Apatosaurus as they navigated their prehistoric world.
Each fossil tells a story, providing significant insights into the trials of these magnificent dinosaurs.
When you think about the extinction of Apatosaurus, it’s fascinating to explore the various theories, like volcanic activity and asteroid impacts.
Comprehending its legacy not just sheds light on dinosaur evolution but furthermore highlights its presence in popular culture and notable museum exhibits.
These discussions reveal the intricacies and ongoing debates surrounding this iconic dinosaur.
The extinction of the Apatosaurus, like many other dinosaurs, remains a topic of intense study and debate among paleontologists. Various mass extinction theories highlight the complex factors that contributed to their demise approximately 66 million years ago.
Key hypotheses include:
These elements combined likely made the Apatosaurus particularly vulnerable. The loss of vegetation would’ve severely impacted their food supply, leading to a decline in their populations.
Fossil evidence supports the idea that environmental changes played a crucial role in the extinction of large dinosaurs, including the Apatosaurus. Comprehending these extinction theories not only sheds light on the fate of this magnificent creature but similarly helps us grasp the intricate web of life that existed during the Mesozoic era.
Grasping the extinction of the Apatosaurus provides valuable insights into the broader narrative of dinosaur evolution. This colossal sauropod exemplifies key evolutionary adaptations that allowed large herbivores to thrive in diverse ecological niches. Fossil evidence reveals how Apatosaurus, distinct from its former classification as Brontosaurus, played a vital role in comprehending the lineage and evolution of sauropods.
To illustrate its ecological significance, here’s a quick overview of Apatosaurus:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Dietary Diversity | Herbivorous, foraging for vegetation |
| Anatomical Features | Long neck and sturdy tail |
| Ecological Role | Maintained vegetation balance |
| Evolutionary Insights | Adaptations for immense body size |
Apatosaurus showcases the anatomical features necessary for sustaining its size, like specialized weight distribution. Its diverse feeding strategies highlight how these dinosaurs adapted to their environment, contributing to their survival. Ongoing research into Apatosaurus fossils continues to enrich our comprehension of dinosaur diversity and the complex ecological dynamics of the Late Jurassic period.
Apatosaurus has left a lasting mark on popular culture, fascinating audiences through its portrayal in films, literature, and educational content. This gentle giant has become a staple in various media, enchanting both kids and adults alike.
You might’ve seen Apatosaurus in:
The 1993 film “Jurassic Park” showcased Apatosaurus as a key attraction, further cementing its place in modern pop culture.
Confusion with the Brontosaurus often leads to misrepresentation, but recent discussions have revived interest in Apatosaurus, highlighting its importance.
You can find an array of Apatosaurus merchandise celebrating this iconic species, catering to collectors and enthusiasts.
As the comprehension of these ancient creatures evolves, so does their representation in popular culture, ensuring that Apatosaurus remains a beloved symbol of the Jurassic period for generations to come.
During exploring notable museum exhibits, you’ll discover fascinating displays that highlight the Apatosaurus’s significance in both paleontology and natural history.
One of the museum highlights is at the Carnegie Museum of Natural History, where a significant Apatosaurus fossil—including its long-lost skull rediscovered in 1978—offers insights into its physical characteristics.
The American Museum of Natural History showcases an impressive skeleton that emphasizes the dinosaur’s massive size and unique skeletal structure, enhancing public comprehension of sauropod anatomy.
Significantly, the Field Museum in Chicago features a cast of an Apatosaurus skeleton in its Dinosaur Hall, illustrating the importance of this dinosaur in grasping the Jurassic ecosystem.
Recent display innovations reflect the 2015 reclassification of Apatosaurus and Brontosaurus, ensuring that exhibits present the latest paleontological research.
These exhibits not just promote fossil preservation but additionally emphasize visitor engagement through interactive elements.
Many displays highlight the historical confusion between the two genera, utilizing new fossil evidence to educate visitors.
This educational impact encourages a deeper appreciation for the Apatosaurus and its role in our planet’s prehistoric legacy.
The fascinating exhibits of the Apatosaurus highlight not just its physical majesty but furthermore the scientific debates surrounding its classification and legacy. For decades, this gentle giant has been at the center of taxonomy debates and naming controversies. You might be surprised to learn that early misidentifications led many to confuse it with the Brontosaurus, creating classification challenges that persist today.
Consider these key points:
As you explore the Apatosaurus’s story, you’ll appreciate the evolutionary implications of these debates. They shape our comprehension of this remarkable creature while reflecting the broader narrative of how science constantly evolves.
Embrace the expedition of discovery, as each finding uncovers more about the past and our planet’s history.
Recent research has uncovered fascinating insights into the Apatosaurus, reshaping our comprehension of its classification and adaptations.
Ongoing excavations continue to reveal vital details about its ecology and evolutionary history.
You’re about to learn how these findings impact our view of this remarkable dinosaur.
New findings in paleontology have revealed fascinating insights into the Apatosaurus, enhancing our grasp of this remarkable sauropod. Recent studies have clarified the distinctions between Apatosaurus and Brontosaurus, shedding light on sauropod diversity.
Key discoveries include:
These findings have profound implications for grasping Apatosaurus behavior, diet, locomotion, and social structure.
For instance, knowing they foraged in herds helps us appreciate their social interactions and how they might’ve defended against predators. Their diet primarily consisted of vegetation, which highlights their role in their ecosystem.
Collectively, this research paints a clearer picture of Apatosaurus ecology, revealing how these gentle giants thrived in their environment. As you explore further, consider how these insights contribute to our overall grasp of these incredible creatures.
Excavations at sites like Howe Quarry continue to uncover thousands of Apatosaurus fossils, greatly enhancing our grasp of their anatomy and behavior. These fossil excavation techniques are essential, as they provide new insights into the life of this remarkable sauropod. Recent paleontological fieldwork has focused on reclassifying Apatosaurus and Brontosaurus by analyzing 81 sauropod skeletons, revealing complex phylogenetic relationships.
The table below summarizes recent research efforts:
| Research Focus | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Dinosaur Behavioral Studies | Insights into herd behavior and foraging habits |
| Ecological Niche Analysis | Adaptations to various habitats and interactions |
| Sauropod Diversity Research | Comprehension of evolutionary patterns among species |
| Skull Reclassification | Improved models of head structure from 1978 find |
| Ongoing Excavations | Continuous discoveries enhancing fossil records |
As you explore these studies, you’ll find that current research is shedding light on the ecological niches occupied by various Apatosaurus species. This work contributes to a broader grasp of their adaptations and interactions, eventually enhancing our appreciation for sauropod diversity and evolution.
Now that you’ve learned about recent research, let’s explore some additional information about the Apatosaurus.
You’ll find fascinating details on its ecological roles and modern analogs, along with some fun facts that highlight its unique traits.
Comprehending these aspects will deepen your appreciation for this incredible dinosaur.
What makes the Apatosaurus such a fascinating creature from the Jurassic period? This colossal sauropod, likewise known as the “deceptive lizard,” offers a glimpse into a world that thrived approximately 156 to 151 million years ago.
With its impressive size—up to 75 feet long and weighing around 22 tons—Apatosaurus showcases incredible evolutionary adaptations that allowed it to flourish.
Understanding these aspects of the Apatosaurus emphasizes its importance in the ecosystem and reminds us of the delicate balance of life during the Jurassic period.
Through ongoing research, we endeavor to keep this iconic species alive in our collective memory.
Exploring modern analogs to the Apatosaurus reveals fascinating parallels in ecological roles and adaptations among today’s large herbivores. Elephants and giraffes, for instance, showcase similar herbivore adaptations that echo the Apatosaurus’s feeding strategies. These species are integral to their ecosystems, just as the Apatosaurus was in its time.
| Modern Herbivore | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Elephant | Large size, strong social structures, wide habitat preferences |
| Giraffe | Long neck for browsing, solitary or small group living, diverse feeding strategies |
Both elephants and giraffes demonstrate how herbivores exploit high vegetation, mimicking the Apatosaurus’s method of foraging. Their social structures allow for protection against predators, reflecting the herd behavior of this ancient giant. Additionally, all these species require vast territories to meet their dietary needs, emphasizing the critical role space plays in their ecological niches. By comprehending these modern counterparts, you gain insight into the complex interactions and adaptations that shaped the realm of the Apatosaurus.
The Apatosaurus, known for its massive size and gentle demeanor, boasts some intriguing facts that highlight its unique characteristics. This colossal dinosaur, which could grow up to 76 feet (23 meters) in length and weigh around 26 tons (24,000 kg), had a surprisingly small brain—only 4 ounces (125 grams).
In spite of this, its behavior was primarily peaceful as it foraged in herds, showcasing a fascinating aspect of Apatosaurus socialization.
Here are some fun facts about the Apatosaurus:
Understanding Apatosaurus reproduction and feeding habits helps us appreciate its role in the ecosystem.
In spite of past challenges, ongoing research remains crucial for the preservation of this magnificent creature and its unique place in history.
Apatosaurus is special because of its massive size, reaching up to 75 feet. Its peaceful behavior, herbivorous diet, and unique habitat adaptations are highlighted in fossils, showcasing its crucial role in the Jurassic ecosystem.
You’ll find that Brontosaurus classification identifies it as slightly smaller than Apatosaurus, which thrives in diverse habitats. As both share similar diets, Apatosaurus has distinct fossils, showcasing its unique traits and adaptations throughout history.
Apatosaurus faced threats from predators and environmental changes. Extinction theories suggest habitat loss and climate shifts contributed to their decline, whereas fossil discoveries reveal evolutionary adaptations that helped them survive in challenging conditions for a time.
You’ll find numerous Apatosaurus fossil discoveries, with several well-preserved skeletons unearthed. Their unique bone structure and habitat range reveal insights into their dietary habits and historical significance, highlighting their role in comprehending prehistoric ecosystems.
To summarize, exploring the realm of the Apatosaurus reveals just how incredible these gentle giants were. From their towering necks to their crucial role in the ecosystem, they captured the imagination of scientists and enthusiasts alike. As you reflect on their expedition through time, remember the importance of conserving their legacy and the lessons we can learn from their existence. Let’s continue to appreciate and protect the wonders of our planet, ensuring future generations can marvel at the Apatosaurus.